Osmylation-OsO4 (Osmium Tetroxide)
Key Questions
-
Osmium tetroxide is an oxide of osmium.
It has many uses, despite the fact that the abundance of Os in the earth's crust is only 1.5 ppb by mass.

OsO₄ is colourless and has a chlorine-like odour. Most samples appear yellowish because of contamination by yellow-brown OsO₂.
OsO₄ is tetrahedral and nonpolar.

Some of its physical properties are:
- melting point = 40°C
- sublimes at room temperature
- boiling point = 130°C
- solubility in water = 6.2 g/100 mL
- solubility in CCl₄ = 375 g/100 mL
The most common use of OsO₄ in organic chemistry is to convert alkenes to vic-diols.
The mechanism involves a concerted cis addition to form a cyclic osmate ester, which then hydrolyzes to form the diol.
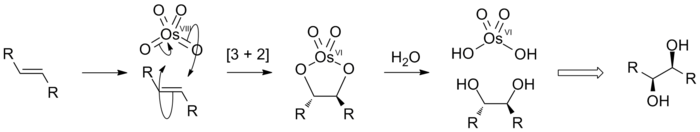
OsO₄ is usually used in small amounts as a catalyst. Reactants such as H₂O₂ are added to regenerate the OsO₄.
OsO₄ is expensive (over $200/g) and highly toxic. The permissible exposure limit is only 2 µg/m³ over 8 h.
OsO₄ can even diffuse through plastic, so it must be kept in glass containers and in a fume cupboard.
-
it is used to make alkenes in to 1,2-diols.
Refer to this site:masterorganicchemistry
-
OsO₄ is a catalyst. MnO₄⁻ is a reactant.
#"OsO"_4"/t-BuOOH/HO"^(-)"Reaction:"# 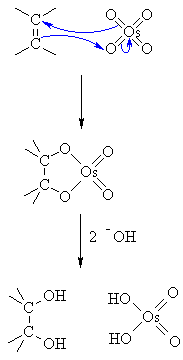
-
The OsO₄ is a catalyst. It reacts with the π electrons of the alkene in a syn addition to form a cyclic osmate ester.
-
The OH⁻ hydrolyzes the ester. This forms the cis-diol and H₂OsO₄.
-
The t-BuOOH oxidizes the H₂OsO₄ and regenerates the OsO₄ catalyst:
t-BuOOH + H₂OsO₄ → t-BuOH + OsO₄ + H₂O
#"KMnO"_4"/NaOH/0°C Reaction:"# 
As with OsO₄, the reaction goes through a cyclic ester to form a cis diol.
In this case, the MnO₄⁻ is a reactant, not a catalyst, because the MnO₄⁻ is not regenerated.
-