Question #b135f
1 Answer
Sep 3, 2015
An inductive effect is transmitted through the σ bonds; an electromeric effect is transmitted through π electrons.
Explanation:
An inductive effect is the effect on electron density in one portion of a molecule caused by electron-withdrawing or electron-donating groups elsewhere in the molecule.
For example, an electronegative halogen atom withdraws electron density from other parts of the molecule through the σ bonds.
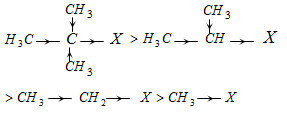
The IUPAC defines an electromeric effect as the movement of electrons from one atom through a π system, as indicated by the curved arrows.

The IUPAC considers the term "electromeric effect" to be obsolete. The preferred term is "substituent resonance effect"

