What are the factors that determine the strength of an acid?
1 Answer
The factors that affect the strength of a carboxylic acid are
- Resonance stabilization
- Electron donating groups
- Electron withdrawing groups
Explanation:
Resonance Stabilization
The ethanoate ion is strongly stabilized by two equivalent resonance structures.
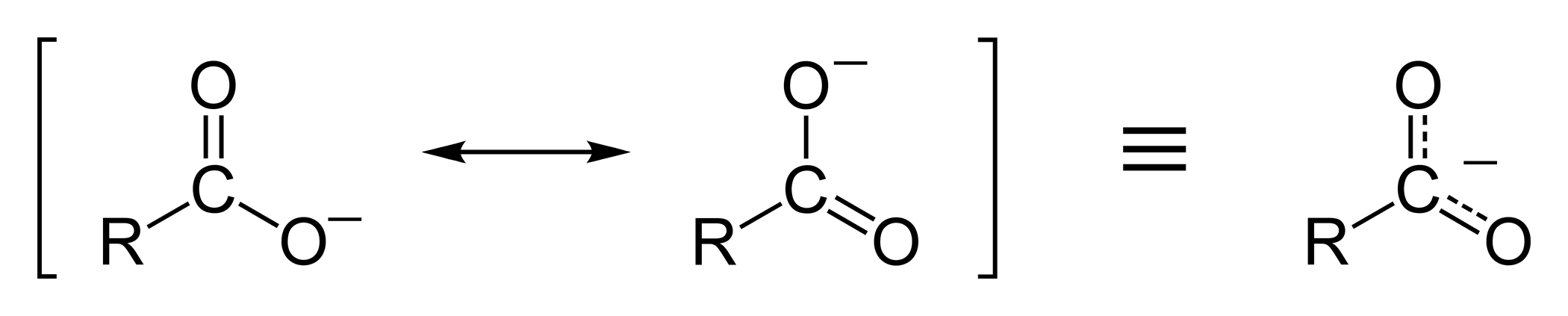
The phenoxide ion is less effectively stabilized.

In three contributors, the negative charge is delocalized into the ring. These are not major contributors because (a) they disrupt the cyclic π system in the ring and (b) O is more electronegative than C.
The ethoxide ion has no resonance contributors.
Electron Donating Groups
Electron donating groups decrease the acidity of an organic acid.
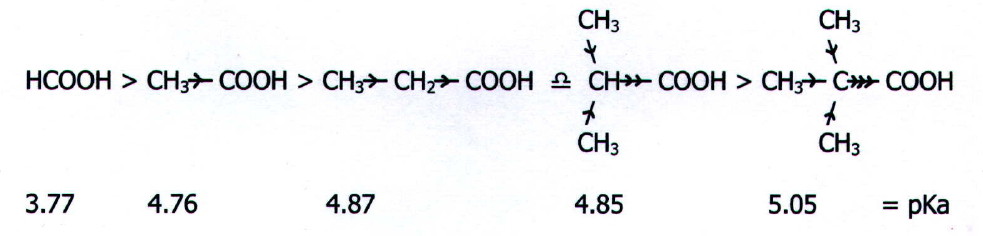
Alkyl groups are electron donating. They tend to "push" electrons away from themselves.
This increases the electron density in the O-H bond. The H atom is more strongly attracted to the O. It is less likely to leave, so the acid is weaker.
Electron Withdrawing Groups
Electron withdrawing groups increase the acidity of an organic acid.

An electronegative atom like Cl can pull electron density toward itself.
This decreases the electron density in the O-H bond. The H atom is less strongly attracted to the O. It is more likely to leave, so the acid is stronger. The more Cl atoms you attach, the stronger the acid becomes.

