What is an ozonide in the mechanism for ozonoide formation?
1 Answer
Feb 15, 2015
An ozonide is the 1,2,4-trioxolane structure that is formed when ozone reacts with an alkene,
The first intermediate in the reaction is called a molozonide.
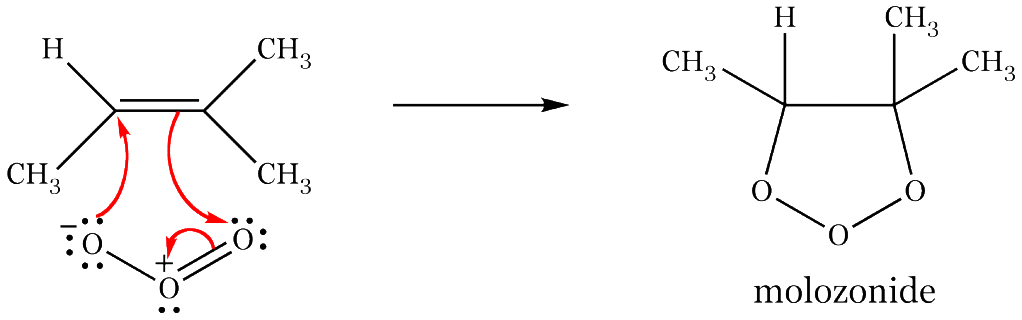
A molozonide is a 1,2,3-trioxolane (tri ="three"; oxa = "oxygen"; olane = "saturated 5-membered ring").
The molozonide is unstable. It rapidly converts in a series of steps to an ozonide.

An ozonide is a 1,2,4-trioxolane. It rapidly decomposes in water to form carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes and ketones.
The video below shows the formation of the molozonide and ozonide intermediates as part of the mechanism.

