What factors affect coupling constants?
1 Answer
The major factors affecting coupling constants are dihedral angles, substituents, hybridization, and ring strain.
Explanation:
The major factors for three-bond couplings between vicinal
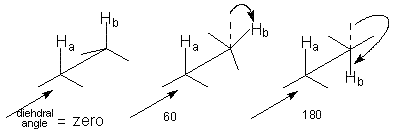
(a) Dihedral Angles
(2 to 5 Hz) for a gauche conformation and 0 for a 90 ° angle
(b) Substituent effects
Electronegative substituents decrease the value of
For example,
Also,
The major factors for one-bond
(a) Substituent Effects
Electronegative substituents increase the value of
For example,
(b) Hybridization
Typical values are 125 Hz for
(c) Ring Strain
Strained rings show unusually large
This is consistent with the idea that the
Typical values are 127 Hz for cyclohexane, 161 Hz for cyclopropane, and 228 Hz for the alkene