How do functional groups affect intermolecular attractions?
1 Answer
Functional groups contribute to dipole-dipole attractions and to hydrogen bonds.
Every functional group is polar. This causes dipole-dipole attractions. If the group contains O-H or N-H bonds, hydrogen bonds are also present.
Common functional groups include
R-X —alkyl halide; R-O-R’ —ether; R-C≡N — nitrile
These all have polar bonds and generate dipole-dipole interactions.
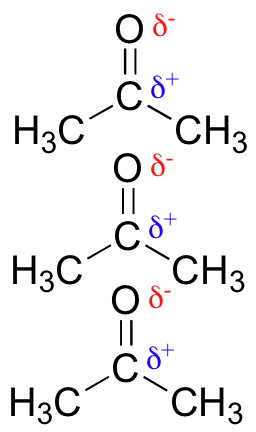
R-CHO —aldehyde; R-COR’ — ketone; R-COOR’ — ester
These have polar C=O groups. They generate stronger dipole-dipole interactions.
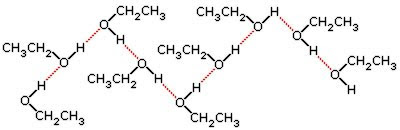
R-OH — alcohol; R-NH₂ — amine
These have O-H and N-H bonds. They generate strong hydrogen-bonding interactions.
R-COOH — carboxylic acid; R-CONH₂— amide
These have C=O bonds as well as O-H or N-H groups. They generate the strongest intermolecular forces.


