Question #d89a9
1 Answer
Decarboxylation is a benefit to the human body because it is a key part of the glycolysis and Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle mechanisms that provide energy for the cells.
The body gets its energy from the oxidation of glucose to carbon dioxide and water.
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + energy
Each of the carbon atoms in glucose is converted into CO₂ in a decarboxylation reaction.
Decarboxylation is the loss of CO₂ from a molecule. An example is
CH₃COCH₂COOH → CH₃COCH₃ + CO₂
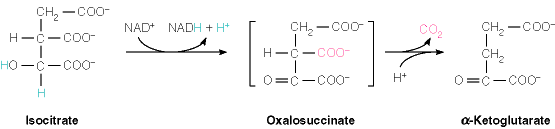
The key decarboxylation steps occur in glycolysis and the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle.

Pyruvate to AcetylCoA

This is the step that feeds into the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle.
Oxalosuccinate to α-ketoglutarate
α-Ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA

Without these decarboxylations, the Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle would grind to a halt, and the cells would lose a major source of energy.

