How does carbon use its #"s"# and #"p"# orbitals to form bonds in ethyne, ethene, and ethane?
1 Answer
Carbon uses its 2s orbital and enough 2p orbitals to form hybrid orbitals that bond to other atoms.
A carbon atom hybridizes by mixing its 2s and 2p orbitals to form new orbitals for bonding. It mixes just enough orbitals to form the σ bonds. Any leftover p orbitals form π bonds.
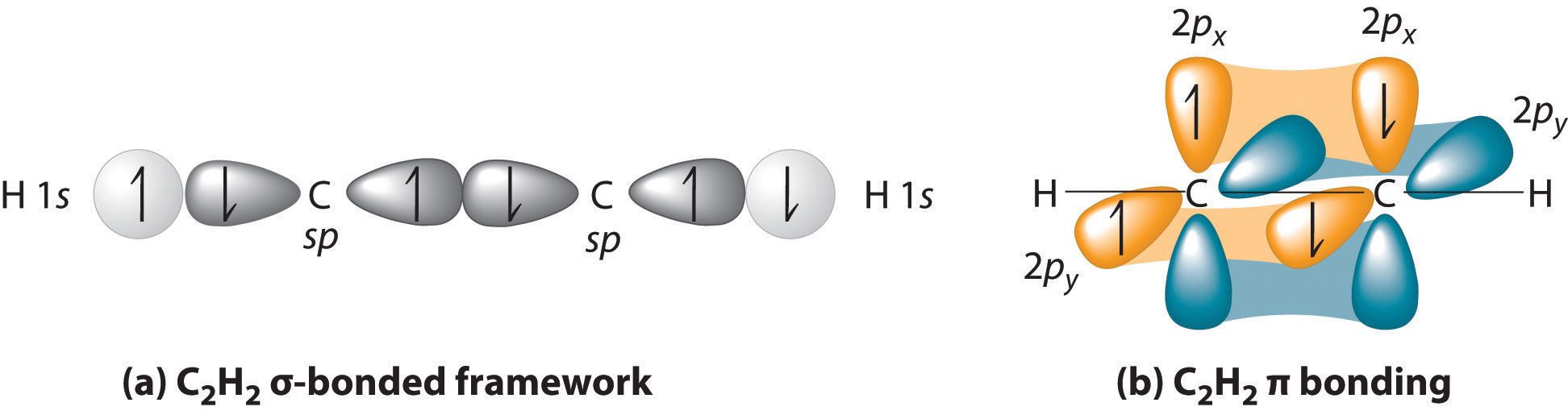
In ethyne, H-C≡C-H, each C atom forms bonds to an H atom and a C atom. Thus, each C atom uses its 2s orbital and one of its 2p orbitals to form two sp hybrid orbitals.
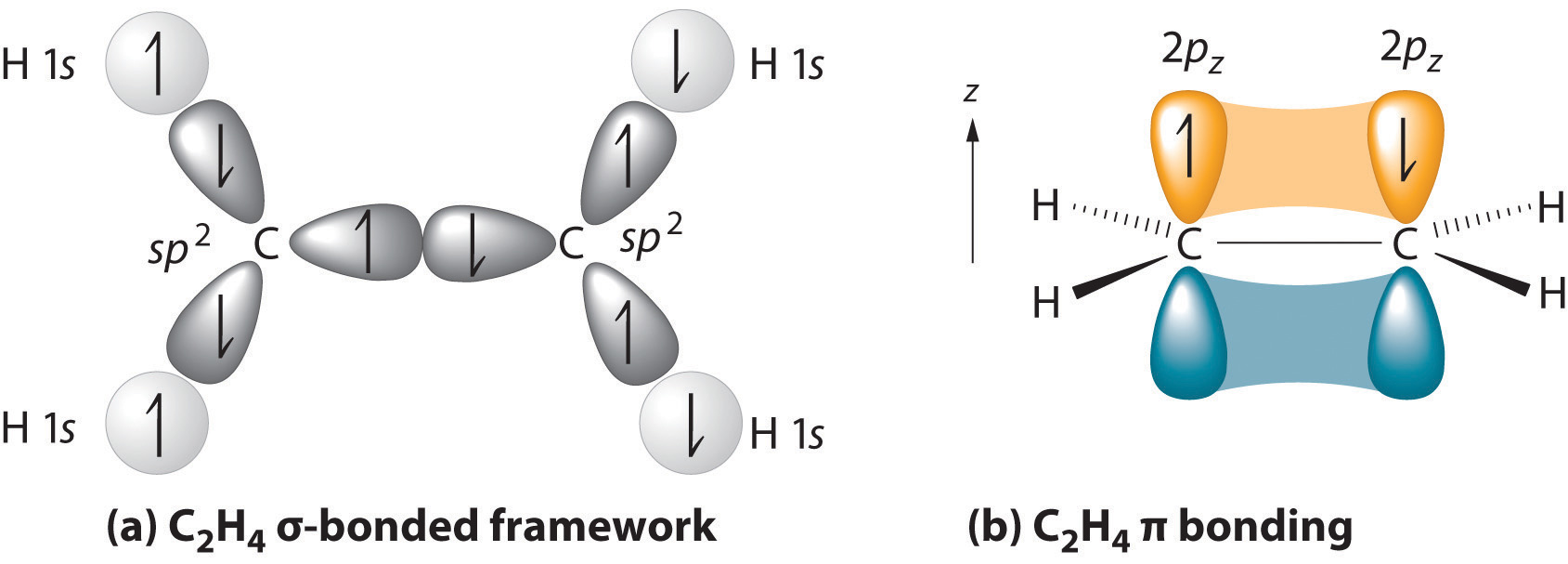
In ethene, H₂C=CH₂, each C atom forms bonds to two H atoms and the other C atom. Thus, each C atom uses its 2s orbital and two of its 2p orbitals to form three sp² hybrid orbitals.
In ethane, H₃C-CH₃, each C atom forms bonds to three H atoms and a C atom. Thus, each C atom uses its 2s orbital and all three of its 2p orbitals.


