What are nucleophilic and electrophilic substitution reactions?
1 Answer
Here's my explanation.
Explanation:
A nucleophilic substitution is a reaction in which an electron pair donor (a nucleophile,
A typical general equation is
where
The mechanisms are different for aliphatic and aromatic nucleophilic substitutions, but the overall result is the same:
A nucleophile
Specific examples are
and
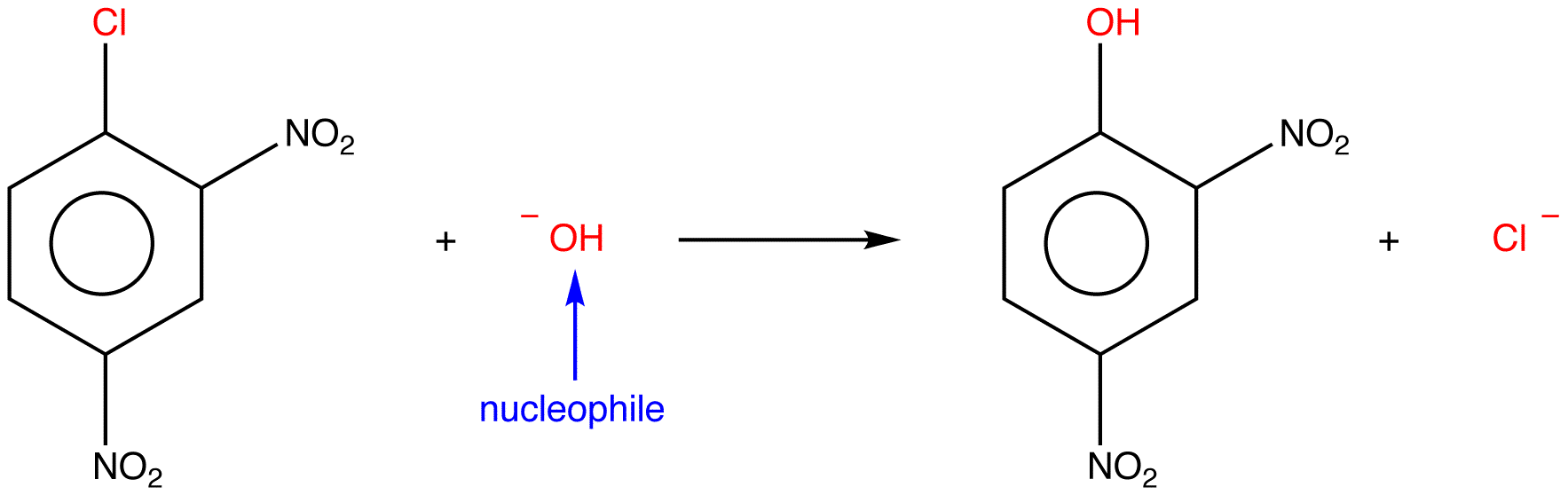
An electrophilic substitution is a reaction in which an electrophile
A typical general equation is
where
An example is an electrophilic aromatic halogenation.

In the above reaction, a
Electrophilic aliphatic substitutions are relatively uncommon.
One important example is the replacement of the metal atom in an organometallic compound by hydrogen:
The decomposition of a Grignard reagent by acid is an example.

