How would you explain the halogenation of benzene?
1 Answer
The halogenation of benzene is an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction.
Explanation:
Electrophilic aromatic substitution
Electrophilic aromatic substitution is a reaction in which an atom on a aromatic ring is replaced by an electrophile.
A typical halogenation reaction is
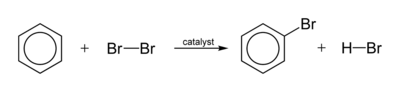
The electrophile is an ion that is generated by the catalyst.
Mechanism
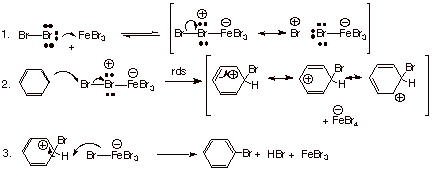
Step 1. Generation of the electrophile
A Lewis acid catalyst, usually
Step 2. Electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring
The nucleophilic π electrons of the aromatic ring attack the electrophilic
This forms
Step 3: Loss of
The
This re-forms the aromatic ring, produces

