How does electrolysis chemistry work?
1 Answer
An electrolytic cell is very similar to an electrochemical cell, but is designed to cause a non-spontaneous reaction to occur by using an external source of DC voltage.
Explanation:
Electrolysis means "to take apart with electricity". To perform electrolysis, one designs an appropriate electrolytic cell, which could very closely resemble an electrochemical cell (also known as a voltaic cell), in that it will have an anode and a cathode plus an electrolytic solution which contacts the two electrodes.
 )
)
One chief difference is that in a voltaic cell, you use a spontaneous reaction to generate an electric potential (voltage); in an electrolytic cell, you use an applied voltage to cause a non-spontaneous reaction to occur.
The electrode that is connected to the negative terminal of the battery (the anode) will be the cathode of the electrolytic cell (still negative, of course). Here, one of the substances in the electrolyte will undergo reduction. In the diagram below,
Meanwhile, electrons are being removed from the anode of the electrolytic cell (positive terminal). Oxidation of a substance in the electrolyte will occur here. (The electrons will arrive at the cathode of the battery where another reduction inside the battery will consume them.)
The diagram shows chloride ions oxidized into chlorine gas
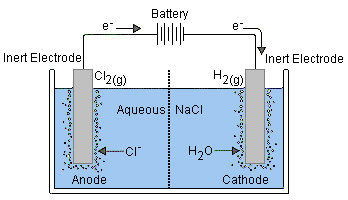
As long as sufficient voltage is applied (equal to the reaction potential of the redox reaction to be carried out, plus a bit more for "overvoltage") the reaction will occur.
The amount of current used will determine the rate at which the product chemicals are produced.
Because the two chemicals are produced at different locations (anode and cathode) they can be drawn off separately, without reacting together.
The electrodes in the electrolytic cell are generally made from an inert material that will not itself undergo either oxidation or reduction. Graphite and platinum are common choices for these electrodes.

