How do Lewis acids and bases differ from Bronsted/Lowry acids and bases?
1 Answer
Lewis acids and bases are defined in terms of being able to accept or donate electron pairs. While Bronsted Lowry acids and bases are defined in terms of being able to accept or donate hydrogen ions (
Explanation:
•A Brønsted-Lowry acid is any substance (molecule or ion) that can donate a hydrogen ion (
•A Brønsted-Lowry base is any species that can accept a hydrogen ion (
Nitrous acid (
• A Lewis acid is defined as an electron-pair acceptor. This means that acids can accept a lone pair of electrons from a Lewis base because the acid has vacant valence orbitals.
• A Lewis acid must have a vacant valence orbital and it can be a cation, such as
• A Lewis base is an electron-pair donor. This means that a Lewis base has the ability to donate two of its electrons to a Lewis acid.
Here's a general depiction of a Lewis acid-base reaction:
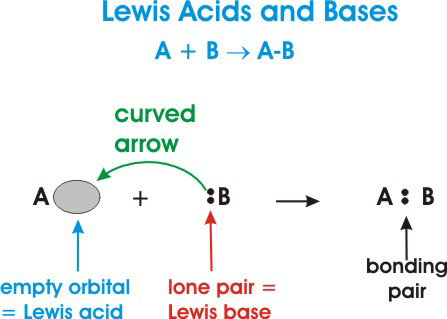
In the diagram above,

