Define a dipole moment?
1 Answer
If you have two charges,
In a polar molecule, there is a build-up of partial negative charge in some parts of the molecule and a corresponding partial positive charge in other areas.
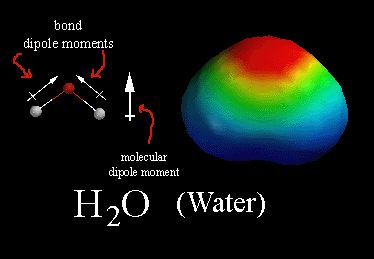
In water, for example, the O atom has a partial negative charge (
The two H atoms each have a partial positive charge (
This separation of charge constitutes a dipole.
In an electrical field, the molecule will experience a torque that causes it to rotate and line up with the field.

The positive charge will be attracted to the negative plate, and the negative charge will be attracted to the positive plate.
The amount of torque depends on the strength of the electric field and on the magnitude and separation of the electric charges.
If each charge has a magnitude
In physics, a moment is the product of a physical quantity and a distance.
That's why we call it a dipole moment.

