How does diversity affect species survival?
2 Answers
More diversity means better chances of survival.
Explanation:
Increased genetic diversity leads to increased chance of species survival. Species with a limited variety of phenotypes and where all members of the species are similar to one another have a smaller chance of coping with environmental variability compared to a species with greater diversity.
In the image below, we have a species with high genetic diversity and one with lower genetic diversity. If a disease is introduced to the area and both species can contact the disease, species 1 is better situated to survive. Even if some phenotypes are not well-adapted to the disease and are wiped out, there are other phenotypes remaining in species 1. This is not true for species 2, a loss of one phenotype dramatically reduces diversity. All it would take is for a single event that the remaining phenotype is poorly adapted to, say a drought, for this species to go extinct.
Its very important to note that natural selection operates ony on phenotype, and selected phenotypes which are controlled by genes can be transferred from one generation to the next. After considerable time, selection pressure may change populations in one of possible three ways: these could be either stabilising/directional/disruptive selection.
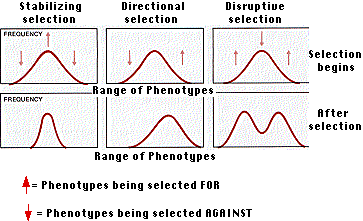
It could be seen from the illustration that maximum range of phenotypic features, i.e. variation are saved after disruptive selection, while after stabilising selection only a narrow range of phenotypic variation would remain in population . Loss of variability due to stabilising selection could increase the threat of extinction.

It is evident from the above illustration that disruptive selection may actually divide a population in subpopulations with distinct characters. For example, zebu cattle of Gangetic plains and other parts of south asia, bisons of european grass lands and yak of himalayas are all descendents of a distant common ancestor:- disruptive evolution allowed them to survive in different climatic conditions in different continents.Then there are other related groups like wild gaurs (indian bison), and semi-domesticated mithuns.
Stabilising selection and decrease in genetic diversity may allow the organism to live within a small, distinct habitat in a certain way. Any change in its environment may threaten its existence.
less diversity means less chance of survival
Explanation:
The Cheetah population of Eastern African is in great danger of extinction because the Cheetah are so superbly adapted to their environment that there is little diversity.
The limited genetic variation within the Cheetah population means that a change in the environment could lead to extinction. There are almost no differences in the genetic pool of the Cheetahs. It is likely that no member of the existing population would have the ability to adapt to the new environment. This would lead to extinction.
Natural selection can not create new variations. It can only cause the extinction of natural variations that are less adapted to the present environment. This loss of natural variation can lead to the extinction of the species if there is a major change in the environment.
The lesser the amount of natural variation the greater chance of the extinction of the species. The likelihood of survival decreases with the a decrease in variation.

