What is Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) and what is its role?
1 Answer
ER is eukaryotic cell organelle.
Explanation:
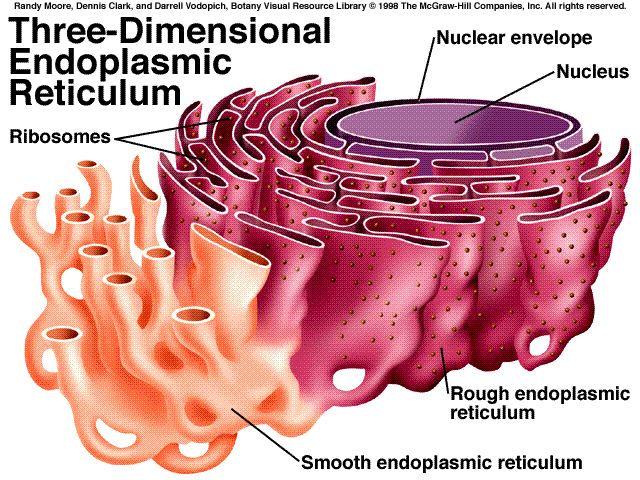
Endoplasmic reticulum is a system of membrane bound tubules, flattened sacs and vesicles which are connected on one hand with the outer membrane of nuclear covering, and on the other with Golgi apparatus.
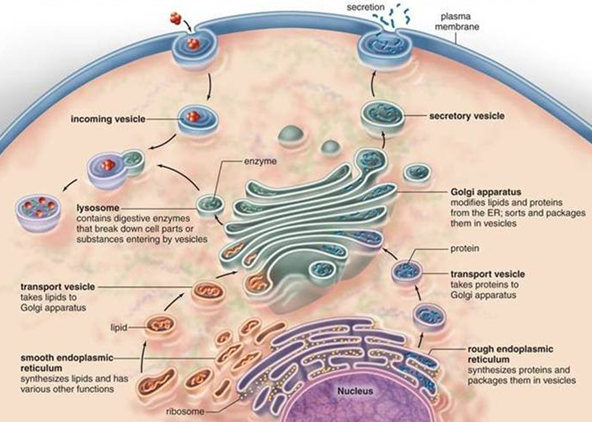
The membrane system of ER could be 'rough' when associated with ribosomes, or 'smooth' when ribosomes are absent from its outer surface.

( )
)
Ribosomes on rough ER produce a variety of proteins: e.g.
- secretory proteins which will be delivered outside the cell
- enzymatic proteins meant for lysosomes
- proteins which will end up on cell membrane
Smooth ER is essentially engaged in synthesis and storage of lipids, including phospholipid.
ER is also involved in modification and transportation of proteins.
Packaged proteins are transported and then stored in secretory vesicles while other molecules are transported to organelles like lysosomes.
Membrane glycoproteins synthesised in ER also eventually reach plasma membrane.
