Given the following data, what is the enthalpy associated with the given equation? ##
Given...
#2H_2(g) + O_2(g) rarr 2H_2O(g)# #;DeltaH_1^@=-484*kJ*mol^-1# #(i)#
#2CO(g) + O_2(g) rarr 2CO_2(g)# #;DeltaH_2^@=-566*kJ*mol^-1# #(ii)#
...what is the enthalpy associated with the reaction...?
#H_2(g) + CO_2(g) rarr CO(g) + H_2O(g)# ?
Given...
...what is the enthalpy associated with the reaction...?
2 Answers
We treat the individual equations as simultaneous linear equations....
and get an endothermic reaction..........
Explanation:
We have:
We want
If I add
But this is EQUAL to
And thus
This is the Hess's law
In the Hess's law you should add both the reactions like this
For example
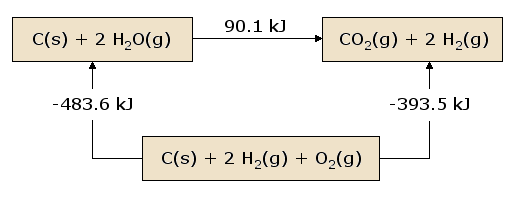
Hess's law states that the addition of total heat absorbed and and released of some reactions is equal to
And you should know that the energy absorbed or released is expressed as
For an equation like
A + B=AB
C+B= CB
A + B = AB
C+ B= CB
Cancel the same reactants on both sides and add the reaction
A + C = CB + AB
Even though its not possible
So if we add the the
Even you can get the
For example if the
C + B = CB
CB = C +B
And consider
A + B
Now again do what we did before
A + B = AB
CB = C + B
CB + A = C + AB
And now add the
Do the same for this reaction
If we cancel the same terms on both side that is
And that's not a sensible reaction and what we wanted
so we do what we did in the above example
Add both the reactions
Cancel the same terms
Now add the
But this is the
not
To caculate the
= 41kJ/mol


