The graphic shows the effective collision cross section, or area:
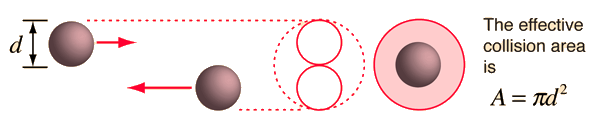
From this we can estimate the diameter of the atoms:
#sf(A=pid^2)#
#:.##sf(d=sqrt(A/pi)=0.36/3.142==0.3385color(white)(x)nm)#
The mean free path #sf(lambda)# is the average distance between collisions.
The expression is:
#sf(lambda=(1)/(sqrt(2)pid^(2)n_v)#
#sf(n_v)# is the number of molecules per unit volume.
We can eliminate this using the Ideal Gas Expression:
#sf(PV=nRT)#
#sf(n_v=(nN_A)/V)#
Where #sf(N_A)# is the Avogadro Constant.
Since #sf(V=(nRT)/P)#
We can write:
#sf(n_v=(cancel(n)N_A)/((cancel(n)RT)/P)=(N_AP)/(RT))#
Substituting this into the expression for #sf(lambdarArr)#
#sf(lambda=(RT)/(sqrt(2)pid^2N_AP))#
#:.##sf(P=(RT)/(lambdasqrt(2)d^2N_A))#
We can now set the condition that #sf(lambda=d)#
#:.##sf(P=(RT)/(sqrt(2)pid^3N_A))#
Putting in the numbers:
#sf(P=(8.31xx298)/(1.414xx3.142xx(0.3385xx10^(-9))^3xx6.02xx10^(23))color(white)(x)"N/m"^2)#
#sf(P=2.837xx10^7color(white)(x)"N/m"^2)#


