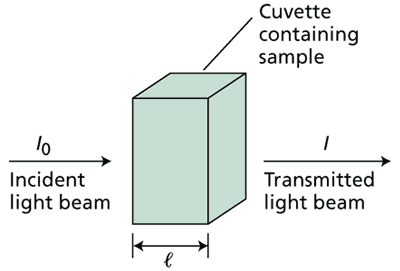
To calculate this, we need to use the Beer-Lambert Law.
#log_10(I_0/I) = A = epsilonCl#
Where #A# = absorbance; #epsilon# = molar extinction coefficient (#dm^(-3)mol^(-1)cm^(-1)#); #C# = concentration (M); #l# = path length (cm); #I_0# = incident light; #I# = transmitted light
 )
)
We can rearrange to solve for the molar extinction coefficient:
#epsilon = A / (Cl)#
The sample transmitted 20%, so we know that #I = 20%# Since the transmitted light is 20% of the incident light, we can take the incident light to be 100% #I_0 = 100%#
#A = log_10(100/20)#
#A = 0.7#
#epsilon = 0.7 / (0.01 xx 1.5)#
#epsilon = 46.7 dm^(-3)mol^(-1)cm^(-1)#
 )
) 
